Yet another interesting comment from Rene Zandbergen yesterday (to my flying potions post) sparked off a furious flurry of bloggery here at Cipher Mystery Mansions. While browsing through a large set of online manuscripts digitized (and hosted) by the University of Heidelberg, he found Cod(ex) Pal(atinus) Germ(anicus) 597 – an alchemical manuscript where a large amount of it is written in cipher (which you can download as a 15MB PDF file). Rene writes:-
Now this is a clear example of a MS where cipher has been used to hide secrets. It leaves me with the question:
Why does the Voynich MS not look like this?
My tentative answer: the Voynich MS isn’t actually just a cipher MS. FWIW.
(–Actually, I have my own answer to this, but we’ll get to that in a minute.–)
It seems to me that (unless Augusto Buonafalce happens to know better) the literature on Cod. Pal. Germ. 597 is pretty thin: even the Karl Bartsch catalogue entry for it (marked 287 here) isn’t much use. The Ms also merits the briefest of mentions on p.355 of the 1994 book “Geschichte der deutschen Literatur von den Anfängen bis zur Gegenwart” (it’s in Google Books). None of which, however, addresses its cipher aspect… but I guess that’s my job. 🙂 So, let’s have a look at it…
The Ms commences on folio 2r with some crossed-out ciphertext above some commentary in a different hand. (Some later pages hold only a few lines of ciphertext, so it seems likely that this originally contained just the ciphertext.) And then on folio 4v, the ciphertext (interleaved with Latin and German plaintext) starts in earnest:-

This is a basic-looking system comprising about 23 symbols, that shows every sign of being a simple (i.e. monoalphabetic) cipher consistent with its date (1426). The cipherbet was designed not for convenience of writing (for there are numerous fiddly characters, including a blocked-in black square), but around an apparently improvised ‘personal shape alphabet’. This points not to a cipher professional (working, say, in a Chancellery) but rather to an amateur cryptographer designing his/her own ‘homebrewed’ system:-
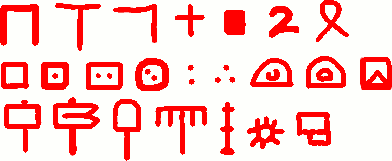
The letter shapes fall into three rough groups (as per the lines above):-
- Abstract shapes / known shapes
- Dots and containers
- Semi-representative (aide-memoire?) shapes (hammers, spade, rake?)
But then, just as you’re getting the hang of that, a completely different monoalphabetic cipher appears (from folio 6v onwards). This looks to be a refinement of this first system… but this post is getting a bit too long, so I’ll defer discussing that to another day.
Is this a “cipher mystery”? Yes, but only a very temporary sense, for I find it terrifically hard to believe that this wasn’t picked up by one or more of the numerous 19th century German codebreaking historians and cracked in a trice (or perhaps even a millitrice). Tony Gaffney would surely munch such a light confection before breakfast. 🙂
Finally, to respond to Rene Z’s question: why does the Voynich Manuscript not look like this? I’d prefer to start by looking at what this does resemble: Giovanni Fontana’s lightly-enciphered books of secrets, which were also from very same period. This mixing of text and ciphertext also occurs in Buonaccorso Ghiberti’s copy of his famous grandfather’s Zibaldone, which has some sections in a simple cipher, most notably what Prager & Scaglia call the “secret hoist” (on folios 95r and 98r of BR 228, for which see “Brunelleschi: Studies of his Technology and Inventions”, pp.67-70). From the simplicity of that cipher (“use the previous letter in the alphabet”), I’d suggest that Buonaccorso probably copied this from an older document, one probably made in the 1430s or 1440s (Lorenzo Ghiberti died in 1455).
Remember that this was the century when paper began to become affordable, and when ordinary people began to develop their own ciphers: and although it has become fashionable to criticize the development of individualism in the early Renaissance, I think it is fair to say that the desire to keep secrets for personal / familial gain runs in close parallel with this. Ghiberti, Fontana and the author of Cod. Pal. Germ. 597 all seem vastly similar in this respect.
Returning to Rene’s initial question, then, I suspect the correct question to be asking should be: why does the Voynich Manuscript not look like any of those ciphered manuscripts?
My own answer is that it is probably because the VMs will turn out to be from circa 1460 (i.e. 20-30 years after all of the above), and its author seems to have benefitted from contact with the sophisticated code-makers in the Milanese Chancellery, who developed and refined ideas in their own cryptographic bubble. Really, the VMs is from a very specific time and place – far too clever to be early 15th century, but still strongly mindful of what earlier ciphers looked like.
Thanks, Nick! Let us know when you or Tony have solved some of it. I wonder what Adam Maclean knows about it too.
Feeling lazy today,
Dennis
That’s a curious document… in particular, I wonder why some pages are seemingly crossed out, and what the animal drawings represent. I look forward to hearing about what it all might mean– some of those symbols in the first cipher might stand in for the planetary symbols which represented substances in alchemy.
After supper –
Top line D T ? K A ? F
Second line B E N M ? ? O O U
Third line S W P R L I U
Using the above produces ‘kupfer’ (copper); ‘merkuri’ (mercury); ‘silberron’ (silver); etc
But my Germans only as good as my Italian – so I can’t read it & got lost with the chw ch tz ??? etc.
Back to Bellaso
Regarding Rene’s question “why does the Voynich Manuscript not look like any of those ciphered manuscripts?” –
My half baked theory is its an accidental case of ‘Chinese whispers’ in writing.
Hi Tony,
Once I’ve transcribed decent lumps of both CPG597 ciphers, I’ll pass them on to you, they should break pretty easily (he says). 🙂
For the VMs, Chinese Whispers doesn’t sit particularly well with the clear, purposeful handwriting. I’m reasonably sure that it’s a combination of verbsoe cipher (hence all the qo / ol / al / or / ar pairs), a restricted polyalpha (say, where part of the alphabet changes state, but part remains the same) and shorthand abbreviations/contractions. That would explain the unusual statistical properties we see… but it would be a r’ght b’stard to crack. Oh well!
Good luck with the last one of the Bellaso set!
Cheers, ….Nick Pelling….
Nick
It’s not half baked any more – you’ve just convinced me I’m right – picture a novice scribe working by candlelight – he is copying a copy of a document in a language he does not know written in characters only some of which he recognises – the result is exactly what you describe – his own hand is purposeful and clear – parts of the alphabet remain the same whilst others are changed etc. etc.
I must write a book on this …. now quickly quockly quokely quokedy-where’s that list of publishers
Hi Tony,
Don’t breathe the fumes! That way lies only madness and the ghosts of book deals past! 🙂
Cheers, ….Nick P….
corrections to previous –
top line DTWKACF
second line BENMGZOOU
third line SHPRLIU
the 2 O’s and U’s are the same symbol badly drawn
Q is represented by a symbol that looks like a lower case q
Nick:
I have a verifiable solution to the VMS script. I know, I know, but, yes, I really do have a valid proof. I’m looking for a 2~4 hardy souls willing to come together (virtually) to translate and fully document the manuscript. As the “writing” is not what everyone thinks it is the translation will take some time. If anyone earnestly wants to unseal this document and publish drop me a line.
Hi VC,
Please email me direct, I’d be happy to be a constructive part of any such effort – [email protected]
Cheers, ….Nick Pelling….
Well, the O’s on the second line (red pictographs shown) are 2 different symbols, not the same. And the U’s on lines 2 and 3 are definitely not the same.
The ciphertext / picto-text is apparently Templar / Masonic.
Nick: I think this exemplifies the fact that the Voynich manuscript cipher alphabet much more closely resembles the 15th century Milanese diplomatic cipher alphabets than the alternatives; when you look at other cipher alphabets you just don’t seem the same degree of similarity. And whilst JKP may argue that there is more similarity with latin shorthand I haven’t yet seen the evidence.
@Mark
Maybe I misunderstood you here, but at second glance, it’s more similar than you think. Some you see in the NSA report of 1978.
He even took some of them one-to-one. If it has the same meaning I’ll leave it.
But I have found that he gave several signs a multiple meaning. Incidentally, this is pretty sticky, as it causes confusion
Published the ‘correct’ decipherment table on this page:
http://voynich.webpoint.nl/?page_id=5458
Davidsch: From my perspective that is interesting as it relates to my research. Firstly the symbols used are very different from the symbols you see in the Voynich or the Tranchedino. Also you say it is a simple substitution cipher. My understanding is that the most advanced ciphers of the period were diplomatic ciphers, I would be very interested to see counter examples of to. This would lead me to believe that this text and its author had little impact on the Voynich.
@Davidsch
Sorry, your ‘correct’ decipherment is really far from beeing correct.
On your website you wrote: “The used language is “bastarda”, bairisch.” There is no such “bairisch” language at all. Bastarda is a kind of writing system in the late Middle Ages and has absolutely nothing to do with Bavarian dialects or any other language.
Apart from many other false interpretations on your site: why don’t you just verify your own “decipherments” of a very well known and searched codex before you post them? Serious scholarly research would have lead you to the correct interpretation.
Davidsch:
“czaichen” doesn’t mean “Küche”, but “Zeichen”, i.e. the zodiac sign of Virgo (end of August/ September).
@Thomas: thanks, now changed.
@Charlotte Auer: aha, so nothing is right and there are many false interpretations?
I am sorry if my work offended you, but I do not understand why you are so angry, perhaps you can tell me what more is wrong in my “decipherments” and why is that between quotation marks?
So, I immediately went to your home page http://voynichms.de/index.html and you starts with an error yourself:
“Die spätmittelalterliche Handschrift mit der Bezeichnung Beinecke MS 408 – weltweit besser bekannt unter dem Begriff “Voynich Manuskirpt””
We both know that there exists no Manuskirpt.
Please work on that first and then come back with some relevant issues.
Nick: Another very interesting post. I, of course, was pleased by the quote “its author seems to have benefitted from contact with the sophisticated code-makers in the Milanese Chancellery, who developed and refined ideas in their own cryptographic bubble” This very selective quote that I have made tallies with my musings as you know.
You have so many interesting posts, it is quite impressive.
Nick: So has someone deciphered this or not?
I think the Voynich is not like this, because:
1) This is an invented alphabet distinct from the standard kind of symbols used in diplomatic ciphers of the time.
2) The Voynich alphabet was invented in part so that it flows and especially as it is a verbose cipher symbols tend to be grouped together such that they flow easily one into another.